The production methods of Soda Ash (sodium carbonate) have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the “best” process depends on resource conditions, environmental requirements, cost control, and industrial supporting facilities.

Ammonia-soda process (Solvay process)
Features
Advantages:
mature process, cheap raw materials (salt, limestone), suitable for large-scale production.
shortcoming:
Low raw material utilization rate (only 75% Sodium Chloride utilized);
Generates large amounts of Calcium Chloride waste residue and wastewater, causing environmental pollution;
Ammonia needs to be recycled and consumes a lot of energy.
Production process diagram
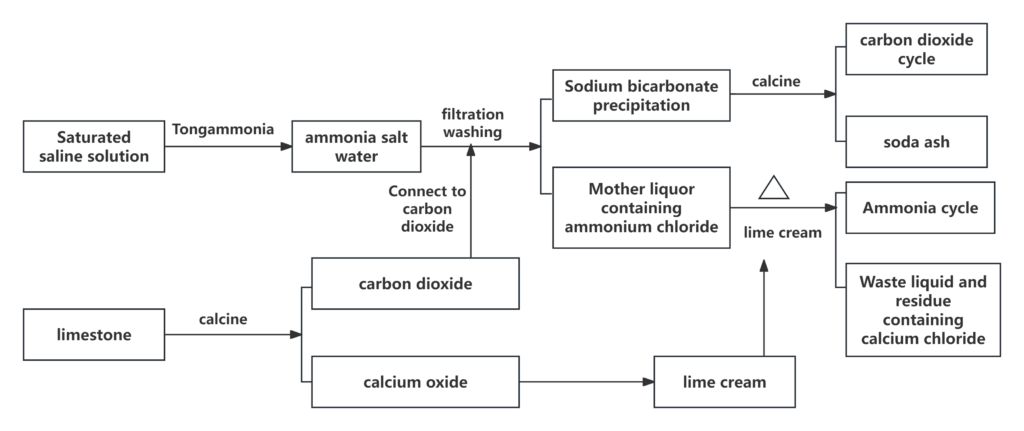
Applicable scenarios
Resource-rich areas (such as close to salt and limestone mines);
Traditional industrial areas that are sensitive to initial investment but have low environmental protection requirements.
Joint alkali production method (Hou’s alkali production method)
Features
advantage:
High raw material utilization rate (Sodium Chloride utilization exceeds 96%);
No waste residue (by-product Ammonium Chloride can be used as fertilizer);
Integrated resource cycling (synergy with synthetic ammonia plants, enabling CO₂ and NH₃ reuse).
shortcoming:
Complex operation requiring precise control of temperature, concentration, and other parameters;
Dependent on synthetic ammonia plant infrastructure.
Production process diagram
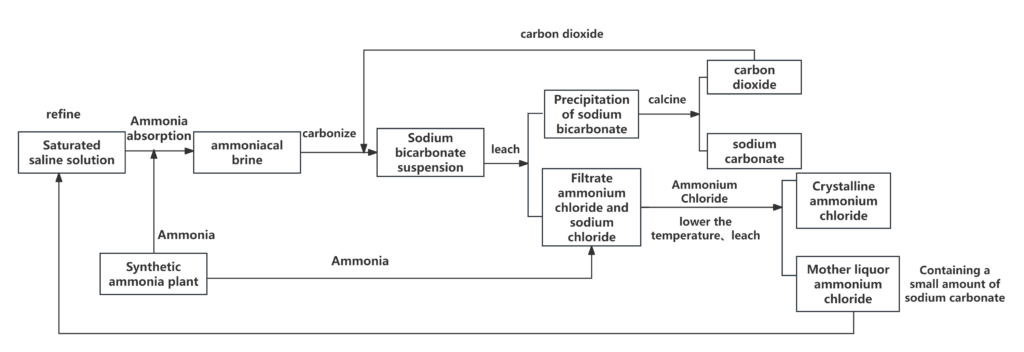
Applicable scenarios
Regions with synthetic ammonia industry chain (such as China and India);
A modern chemical park that focuses on environmental protection and resource recycling.
Natural alkali ore processing method
Features
advantage:
Simple process with low energy consumption and minimal pollution;
Cost-efficient direct mining (such as the Green River Basin in the United States).
shortcoming:
Geographical Limitations:
The availability of natural alkali ore is restricted to specific geological regions, limiting the widespread adoption of this method.
Quality Variability:
Fluctuations in the quality of natural alkali ore can impact the purity of the final soda ash product.
Production process diagram
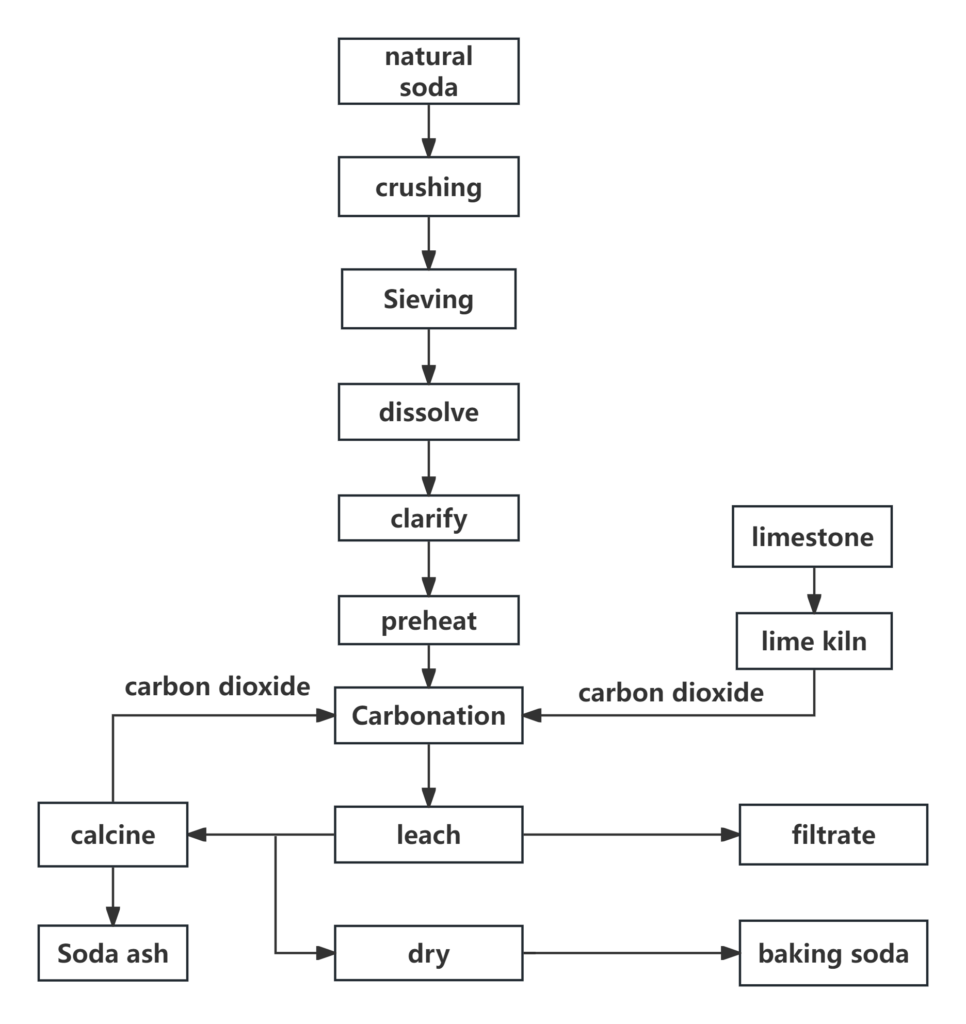
Applicable scenarios
Areas with abundant natural ketone reserves (such as the United States, Türkiye, Inner Mongolia, China);
Green production enterprises that pursue low cost and low carbon emissions.
Comprehensive comparison and selection suggestions
| Evaluation Dimension | Ammonia Alkali Method | Hou’s Method | Natural Alkali Method |
| Raw material utilization rate | Low (~75%) | High (>96%) | Extremely high (direct processing) |
| environmentally | Poor (large amount of waste residue) | Better (resource recycling) | Best (with minimal pollution) |
| cost | Centre | Medium (requires synthetic ammonia matching) | Lowest |
| technical difficulty | Low | High | Low |
| Geographic dependence | Low (readilyavailableraw materials)) | Medium (requires synthetic ammonia plant ) | Extremely high(requires alkali ore) |
Conclusion
Environmental protection and resource efficiency are preferred:
Choose Hou’s alkali production method (suitable for areas with synthetic ammonia industry) or natural alkali mineral processing (in areas with mineral deposits).
Priority on Cost and Scale:
When the natural alkali ore is abundant, choose the natural alkali method, otherwise choose the ammonia alkali method (short-term low cost, but the environmental cost is borne).
Modern industrial trends:
The natural ketone method is dominated (such as 90% of soda ash in the United States comes from this method);
The combination of Hou’s method + natural alkali method (the future direction of resource circulation and low-carbon production).
Sample application scenarios
Inner Mongolia, China:
Natural ketone ore is rich, and natural ketone processing method is preferred.
India/Southeast Asia:
The synthetic ammonia industry is developed and suitable for promoting Hou’s alkali production method.
Traditional European industrial zones:
gradually phase out the ammonia alkali method and switch to imported natural alkali or upgraded joint processes.
Summarize
There is no absolutely “best” method.The optimal production method must be determined through a comprehensive evaluation of resource endowment, environmental regulations, and industrial chain infrastructure:
Natural Alkali Ore Regions:
Opt for the natural alkali method for its cost – effectiveness and environmental friendliness.
Areas without Natural Resources but with a Balanced Industrial Chain:
Choose Hou’s method to achieve a balance between efficiency and environmental protection.
Short – Term Transition or Resource – Constrained Areas:
The ammonia – soda method may be retained, but enhanced pollution control measures are essential.
